The IVF Process
The in-vitro fertilization (IVF) is a set of procedures to treat fertility issues and assist with the conception of an embryo that will be transferred into the surrogate mother’s womb to develop to maturity and become a child. Before starting the actual fertility procedures, a fertility expert has to examine the Intended Parents to determine if it is the Intended Mother and/or the Intended Father who will provide the required genetic material for the gestational surrogacy. This part of the process can be done in the Intended Parents’ country in a Fertility Clinic which will communicate the results to ISC’s partner Fertility Clinic in Kazakhstan or Kyrgyzstan.
Note
Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan’s laws recognized the gestational surrogacy to be legal therefore make it mandatory that at least one of the Child’s Legal Parent to be, be one of the donors. The DNA test will be used as proof of filiation with the Child
IVF Step-by-Step
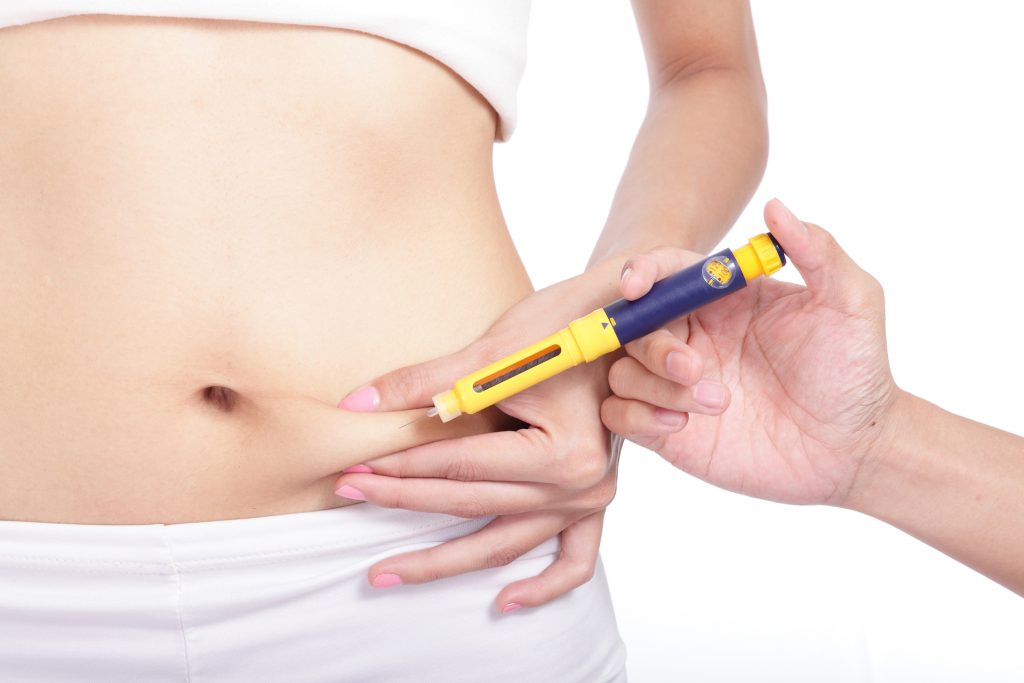
In the case that the Intended Mother is the parent-donor, she receives fertility treatments in her country or in Kazakhstan or Kyrgyzstan to stimulate the production of ovocytes. If she is not fertile, donated ovocytes are used for this procedure in which case, it is the Surrogate Mother who undergoes the fertility treatments to prepare her body to be impregnated with the embryos. Drug induced ovarian stimulation will begin during your menstruation (usually within the first three days of the period). The drugs are administered via injections into the abdomen using a very short and fine needle. Once the first dose is administered and the injection procedure is explained, some patients may inject the remaining doses themselves, or if they request, can attend the clinic on a daily basis for the specialist nurse to do so. Although some variations occur from person to person, the stimulation treatment generally lasts 8 to 12 days. On certain days during the ovary stimulation procedure, scans are required in order to monitor the follicular development. The examination involves an ultrasound screening to evaluate the quantity and size of the developing follicles. If an adequate size and quantity of follicles (at least three,18 mm in size) are detected on the ultrasound and blood hormone levels are suitable, then, in the final stage, an injection to cause ovulation (generally containing human chorionic gonadotropin- HCG) will be administered to ensure control the ovulation time. The timing of this injection is very important because egg collection will begin 35-36 hours after.
When the eggs are stimulated for a pregnancy, they become mature at which stage they are called ovocytes. The ovocytes are retrieved from either the mother or the donor. This procedure is done with the help of a thin needle and a vaginal ultrasound. Afterward, the Embryologist removes the fluid from the follicles, the ovocytes are then removed from the follicular fluid.
Egg collection is performed under anesthesia, the patient is sedated with a very mild anesthesia, and follicle fluids around the ovaries will be aspirated with the help of an ultrasound to guide. The embryologist will then separate the eggs inside the follicles under a microscope, providing an oocyte count for the doctor and patient.
Once the surrogate and intended mother or egg donor all have their cycles coordinated together, the injectable medication will be administered for endometrial stimulation. Some surrogates have complaints of hot flushes, moodiness and headaches.
Estradiol / Estrogen is a medication that is used to thicken the endometrial lining to prepare for the implantation process. This medication begins approximately two weeks prior to embryo transfer and is continued for approximately 10 weeks after embryo transfer depending on the clinic’s protocol. This hormone can be taken in a number of forms: oral tablets; injection, or; adhesive patch; but most IVF clinics use the injection form. Side effects may include, but are not limited to, weight gain and headaches. Each surrogate will receive further instructions on how to administer these injections by the clinic.
During the endometrial stimulation phase surrogates will be required to have a blood test and ultrasound performed on day seven or as directed by the clinic. Some clinics will require the surrogate to have their day seven ultrasound at their clinic only. Other clinics allow the surrogate to remain in their home area until the day of embryo transfer. Until a clinic is chosen, the surrogate will not know the exact protocols she will be asked to follow, but she will be informed as quickly as possible.
The blood tests and ultrasounds will help the clinic determine the thickness of the surrogate’s endometrial lining. Once the endometrial lining is at the appropriate thickness and the intended parent or egg donor are ready to have the egg retrieval, the surrogate will be required to start some form of Progesterone to assist with and sustain implantation and pregnancy.
Progesterone is a hormone women normally produce in our ovaries, but in a surrogacy the addition of supplemental Progesterone is essential to “warm up” the uterus until the body produces this hormone on its own. The form of Progesterone may be in an oil-based, intramuscular injection form or vaginal suppository per the clinic’s orders.
This medication begins approximately one week prior to the embryo transfer and is continued for approximately ten weeks after embryo transfer. Side effects may include, but are not limited to, fatigue, breast tenderness and mild uterine cramping, like being “super pregnant”.
All these medications are extremely important and MUST be taken as instructed by the clinic, or otherwise there is a risk of comprising the IVF cycle, having a miscarriage and being in breach of contract. Please remember, each clinic varies slightly in their protocol.
PLEASE NOTE THAT THERE ARE POTENTIAL RISKS INHERENT WITH ALL ASPECTS OF THE SURROGACY MEDICAL PROCESS AND PROCEDURES, INCLUDING TAKING ANY MEDICATION. IT IS THE SOLE RESPONSIBILITY OF THE SURROGATE TO INVESTIGATE ALL SUCH RISKS AND TO DISCUSS ALL MEDICAL ISSUES WITH THE PRIMARY PHYSICIAN
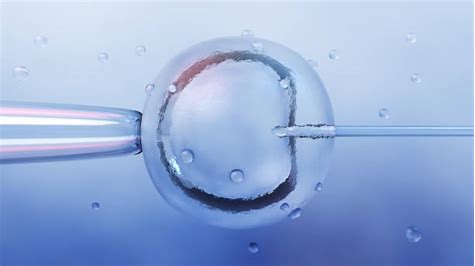
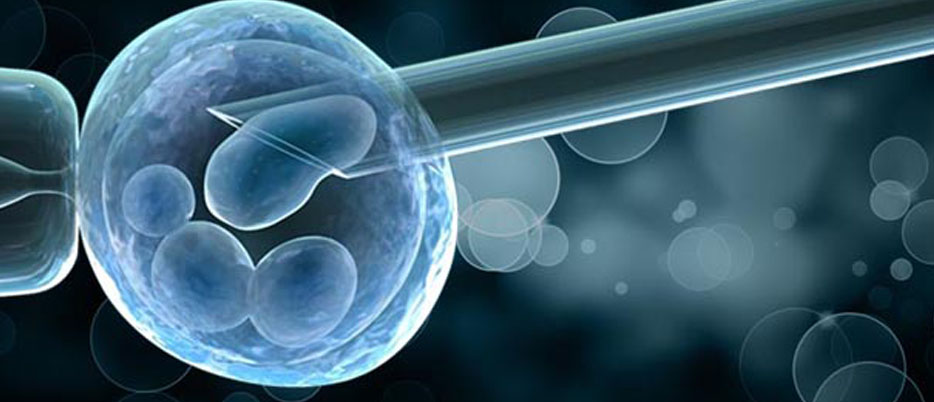
For the fertilization of the ovocytes, a secured sperm is used. This sperm can be from your partner or a donor. The sperm is directly injected into the ovocytes using the ICSI method that is perform by an embryologist by using a special needle to inject only a single sperm into each egg. The fertilized egg is put into a special culture environment and will be examined about 16-18 hours later to see if fertilization has been achieved. The procedure increases the chances of fertilization and therefore conception. After the Embryologist will place the fertilized eggs in the incubator monitoring the development of the embryos between 3-5 days.

The last step of the IVF treatment is the embryo transfer. After monitoring the developed embryo for 5 days, the healthiest ones are selected to be implanted in the Surrogate Mother, the other Blastocysts could be frozen in the case another attempt is needed. After the successful transfer and the implantation, the Surrogate Mother stays at the Fertility for 24 hours in order to make sure the impregnation is successful. In the case that the impregnation did not work, a new Surrogate Mother is chosen to go through the entire process. In the case that the parent-donor genetic material is defective, ISC will discuss other options with the Intended Parents in order to still help with their desire to have a child.
